点积和叉积在开发中的实用技巧
最近在开发中遇到了一些几何问题,这些问题非常适合使用向量的点积和叉积进行解决。
例如,在电商页面中经常会用二级菜单延时三角关闭来提升用户体验。当鼠标斜向滑动到二级菜单时,尽管经过了一级菜单的其他行。
本文将介绍向量的点积和叉积,以及如何利用它们解决一些几何问题。
点积
点积也称为点乘、内积、数量积、标量积,英文为 Dot Product。
点积表示向量 a 在向量 b 方向上的投影与向量 b 模的乘积。
这个概念可能有些抽象,先来看看它的公式。
公式
从代数角度看,先求两数字序列中每组对应元素的积,再求所有积之和,结果即为点积。
从几何角度看,点积则是两向量的长度与它们夹角余弦的积。
两个公式涉及到了向量和角度,可以从中推导出以下公式和用途。
- 计算一个向量的长度
- 计算两个向量的夹角的角度
- 评估两个向量的相似性
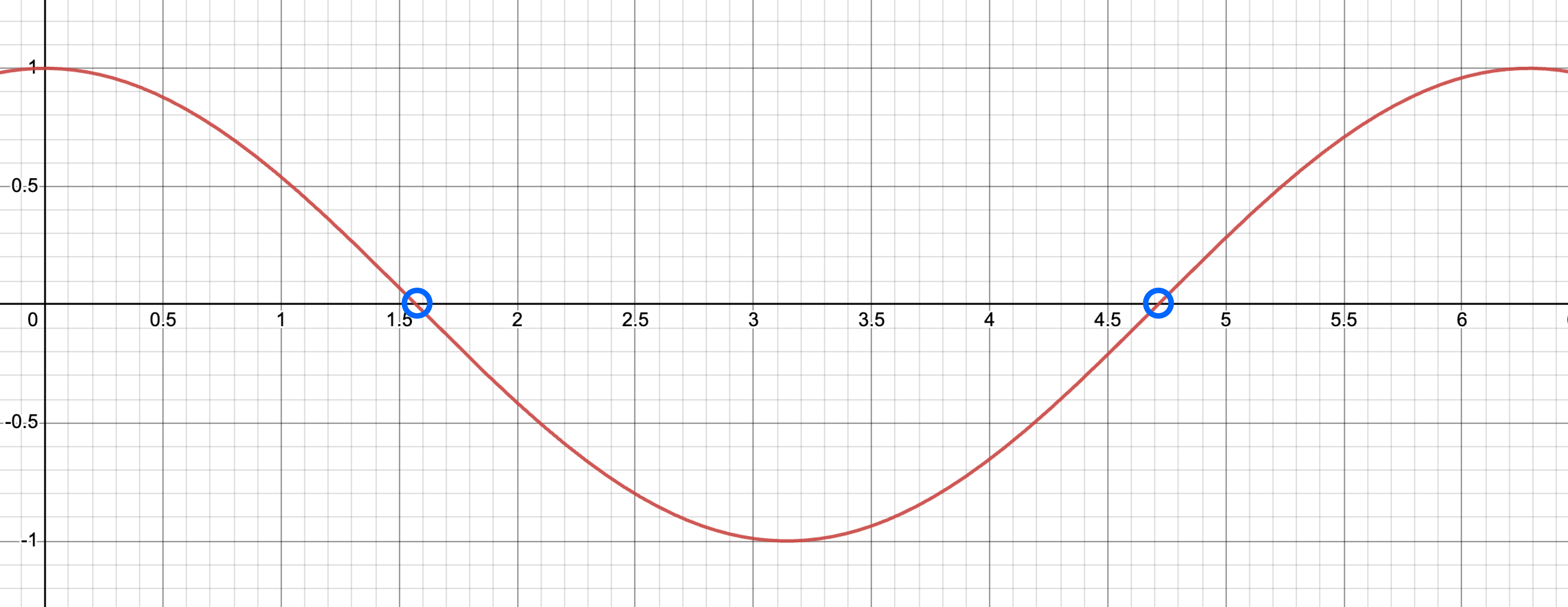
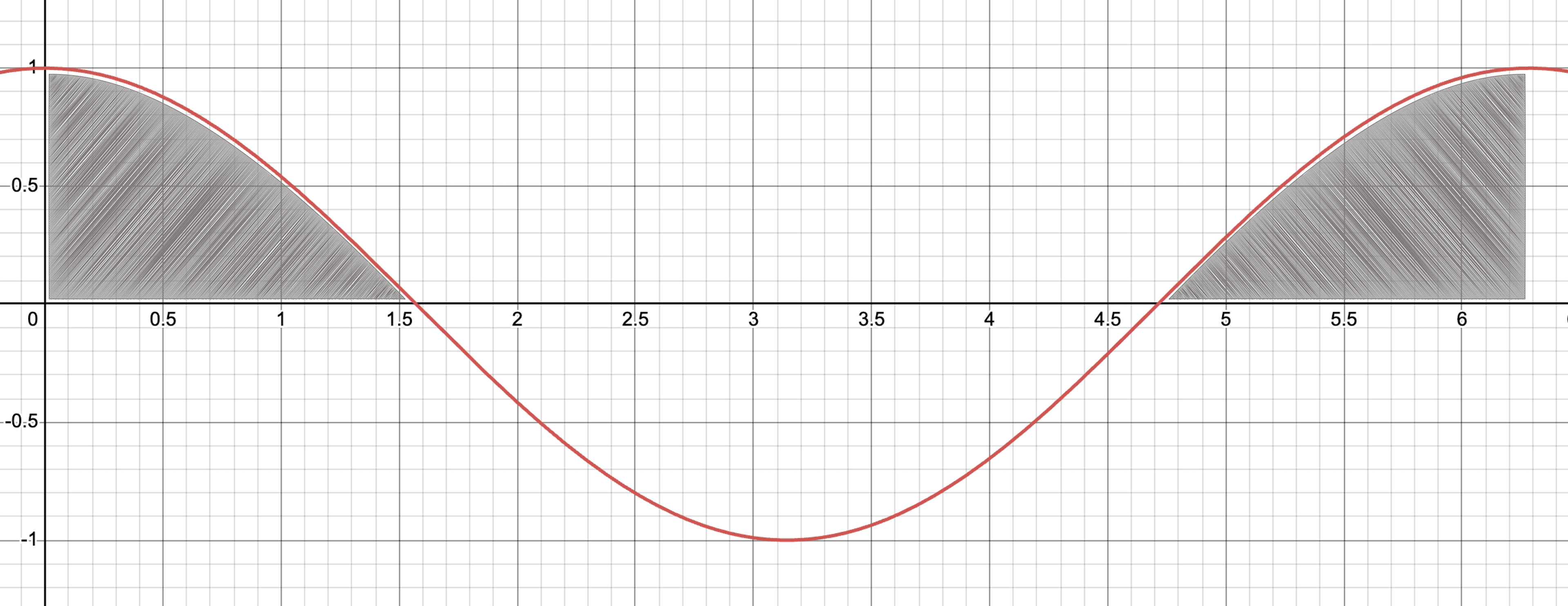
根据余弦函数的图形可以看出,两个单位向量的点积越大,表示方向越相似;如果点积为 0,则表示方向垂直。
两个单位向量的点积的函数图形就是 cos 函数图形.
实用案例
游戏中判断是否被敌人发现,比如星穹铁道/刺客信条等等。
如果敌人的视野范围是面前的 180 度,则通过敌人朝向的方向向量与玩家到敌人的方向向量的点积是否大于 0 来判断是否被发现。
前文提到的右侧菜单的三角感应区域。
其中有三个向量,分别是鼠标原点到鼠标当前位置的向量(蓝色),以及鼠标原点到二级菜单顶部和底部的两个向量(红色),通过比较这三个向量间的夹角,可以判断鼠标当前位置是否在三角形内部。
import "./styles.css" const [v1Path, v2Path, v3Path, v4Path] = document.querySelectorAll('#path-canvas path') const nameRect = document.querySelector('.menu-name').getBoundingClientRect() const bodyRect = document.querySelector('.menu-body').getBoundingClientRect() const v1 = [bodyRect.left - nameRect.left, bodyRect.top - nameRect.top] const v2 = [bodyRect.left - nameRect.left, bodyRect.bottom - nameRect.top] let v3 = [] function line(v, path) { path.setAttribute('d', `M 0 0 L ${v[0]} ${v[1]}`) } line(v1, v1Path) line(v2, v2Path) v4Path.setAttribute('d', `M 0 0 L ${v1[0]} ${v1[1]} L ${v2[0]} ${v2[1]} Z`) v4Path.style.visibility = 'hidden' function cross(a, b) { return a[0] * b[1] - a[1] * b[0] } function dot(a, b) { return a[0] * b[0] + a[1] * b[1] } function length(a) { return Math.sqrt(dot(a, a)) } function theta(a, b) { return Math.acos(dot(a,b) / (length(a) * length(b))); } const v1v2Theta = theta(v1, v2) function update() { line(v3, v3Path) v4Path.style.visibility = (theta(v1, v3) - v1v2Theta) * (theta(v2, v3) - v1v2Theta) >= 0 ? 'visible' : 'hidden' // v4Path.style.visibility = cross(v1, v3) * cross(v2, v3) <= 0 ? 'visible' : 'hidden' } document.addEventListener('mousemove', e => { v3 = [e.clientX - nameRect.left, e.clientY - nameRect.top] update() })
计算坦克炮筒与玩家间的夹角。
import * as THREE from "three"; import { WEBGL } from "three/examples/jsm/WebGL"; import { OrbitControls } from "three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls"; import { Line2 } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/Line2"; import { LineGeometry } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/LineGeometry"; import { LineMaterial } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/LineMaterial"; const search = new URLSearchParams(location.search); const pageSettings = { lookat: !!search.get("lookat") }; const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer(); renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio || 2); renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement); const scene = new THREE.Scene(); const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 ); camera.position.set(2, 10, 7); camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3()); const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement); var direction = new THREE.Vector3(1, 1, 0); var length = 5; var color = 0xfff000; var arrowHelper = new THREE.ArrowHelper( direction, new THREE.Vector3(), length, color ); scene.add(arrowHelper); const light = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff); scene.add(light); const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.5); scene.add(directionalLight); const radialGradientMaterial = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({ uniforms: { radius: { value: 4.0 } }, vertexShader: ` varying vec3 vUv; void main() { vUv = position; gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0); } `, fragmentShader: ` varying vec3 vUv; uniform float radius; void main() { float deg = sqrt(vUv.x * vUv.x + vUv.y * vUv.y); gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 - deg / radius); } `, transparent: true }); const EnemyFieldOfView = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.CircleGeometry(4, 32, Math.PI, Math.PI), radialGradientMaterial ); EnemyFieldOfView.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2; EnemyFieldOfView.position.y = -0.49; const enemyBody = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x28bea0 }) ); const enemyFace = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.1, 0.1, 2, 32), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x28a0be }) ); enemyFace.translateZ(1); enemyFace.rotateX(Math.PI / 2); const enemy = new THREE.Object3D(); enemy.add(enemyBody); enemy.add(enemyFace); enemy.add(EnemyFieldOfView); scene.add(enemy); const ground = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.PlaneGeometry(18, 18), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xeeeeee, transparent: true, opacity: 0.75 }) ); ground.rotateX(-Math.PI / 2); ground.position.y = -0.5; scene.add(ground); const mouseMarker = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xbe3344 }) ); mouseMarker.position.set(0, 0, 5); scene.add(mouseMarker); const line = new Line2( new LineGeometry(), new LineMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff, dashed: true, dashSize: 0.2, gapSize: 0.1, linewidth: 4, defines: { USE_DASH: "" } // worldUnits: true, // vertexColors: true, }) ); scene.add(line); const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(); const mouse = new THREE.Vector2(Infinity, Infinity); function onMouseMove(event) { mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1; mouse.y = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1; } window.addEventListener("mousemove", onMouseMove, false); function updateMouseMarker() { raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera); const intersects = raycaster.intersectObject(ground); if (intersects.length > 0) { const intersectionPoint = intersects[0].point; mouseMarker.position.set(intersectionPoint.x, 0, intersectionPoint.z); } } function updateLine() { line.visible = mouseMarker.visible; // @ts-ignore line.geometry.setPositions([ ...enemy.position.clone().setY(-0.5).toArray(), ...mouseMarker.position.clone().setY(-0.5).toArray() ]); // @ts-ignore line.material.resolution.set(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); // line.geometry.setFromPoints([enemy.position, mouseMarker.position]); line.computeLineDistances(); } function updateEnemy() { if (pageSettings.lookat) { const mouseToEnemy = mouseMarker.position.clone().sub(enemy.position); mouseToEnemy.y = 0; // const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1).applyQuaternion(enemy.quaternion); const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1); const angle = calcAngle(enemyForward, mouseToEnemy); // const normal = enemyForward.cross(mouseToEnemy) const normal = enemyForward.cross(mouseToEnemy).normalize(); enemy.setRotationFromAxisAngle(normal, angle); } } function calcAngle(v1: THREE.Vector3, v2: THREE.Vector3) { return Math.acos(v1.dot(v2) / (v1.length() * v2.length())); } const toDegree = (radian: number) => (radian * 180) / Math.PI; const GUI = document.createElement("div"); GUI.style.cssText = "position: absolute; top: 16px; left: 32px; color: #fff; font-size: 1rem; white-space: pre-wrap"; document.body.appendChild(GUI); function updateGUI() { const mouseToEnemy = mouseMarker.position.clone().sub(enemy.position); mouseToEnemy.y = 0; // const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1).applyQuaternion(enemy.quaternion); const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1); const angle = calcAngle(enemyForward, mouseToEnemy); // const normal = enemyForward.cross(mouseToEnemy) const normal = enemyForward.clone().cross(mouseToEnemy).normalize(); arrowHelper.setDirection(normal); GUI.textContent = ` 点积:${enemyForward.dot(mouseToEnemy).toFixed(1)} 夹角:${toDegree(angle).toFixed(1)}° 旋转轴:${normal.toArray().map((item) => item.toFixed(1))}`; } console.log(arrowHelper); function animate() { requestAnimationFrame(animate); updateMouseMarker(); updateLine(); updateEnemy(); updateGUI(); controls.update(); renderer.render(scene, camera); } if (WEBGL.isWebGLAvailable()) { animate(); } else { const warning = WEBGL.getWebGLErrorMessage(); document.getElementById("container").appendChild(warning); }
这个例子中有两个向量:炮筒方向向量与坦克到玩家的方向向量。 GUI 中不仅显示了两个向量的夹角,还显示了两个向量的旋转轴(黄色),也就是两个向量所在平面的法向量,可以看到旋转轴不是一直不变的,而这个旋转轴的计算就需要用到叉积了。
叉积
叉积也被称为叉乘、外积、向量积,英文为 Cross Product。
叉积表示两个向量构成的平面的法线向量,法线向量与两个向量垂直,方向由右手定则决定。
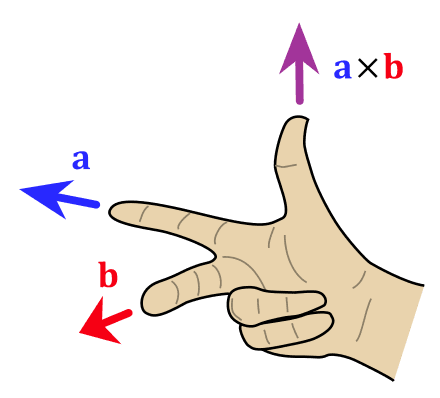
公式
代数公式
几何公式
实用案例
叉积有一个很实用的场景,用于判断一个向量是否在两个向量夹角内的平面上。
红色箭头代表红色与蓝色直线所在平面的法向量,绿色箭头代表绿色和蓝色直线所在平面的法向量,黄色箭头代表红色向量与绿色向量的叉积,也就是这两个向量坐在平面的法向量。
import * as THREE from "three"; import { WEBGL } from "three/examples/jsm/WebGL"; import { OrbitControls } from "three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls"; import { Line2 } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/Line2"; import { LineGeometry } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/LineGeometry"; import { LineMaterial } from "three/examples/jsm/lines/LineMaterial"; console.log(new THREE.Vector3(0, 1, 0).dot(new THREE.Vector3(0, -1, 0))); const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer(); renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio || 2); renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement); const scene = new THREE.Scene(); const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 ); camera.position.set(2, 10, 7); camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3()); const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement); const arrowHelperA = new THREE.ArrowHelper( new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), 7, 0xff0000 ); scene.add(arrowHelperA); const arrowHelperB = new THREE.ArrowHelper( new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), 5, 0x00ff00 ); scene.add(arrowHelperB); const light = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff); scene.add(light); const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 0.5); scene.add(directionalLight); const ground = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.PlaneGeometry(18, 18), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xeeeeee, transparent: true, opacity: 0.3 }) ); ground.rotateX(-Math.PI / 2); scene.add(ground); const mouseMarker = new THREE.Mesh( new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0xbe3344 }) ); mouseMarker.position.set(0, 0, 5); scene.add(mouseMarker); const line = new Line2( new LineGeometry(), new LineMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff, linewidth: 4 }) ); // @ts-ignore line.material.resolution.set(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); scene.add(line); const vecA = new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 5); const lineA = new Line2( new LineGeometry().setPositions([0, 0, 0, ...vecA.toArray()]), new LineMaterial({ color: 0xff0000, linewidth: 4 }) ); // @ts-ignore lineA.material.resolution.set(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); scene.add(lineA); const vecB = new THREE.Vector3(5, 0, 1); const lineB = new Line2( new LineGeometry().setPositions([0, 0, 0, ...vecB.toArray()]), new LineMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00, linewidth: 4 }) ); // @ts-ignore lineB.material.resolution.set(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); scene.add(lineB); const arrowHelperC = new THREE.ArrowHelper( new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), 3, 0xffff00 ); arrowHelperC.setDirection(vecA.clone().cross(vecB)); // arrowHelperC.setDirection(vecB.clone().cross(vecA)); scene.add(arrowHelperC); const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(); const mouse = new THREE.Vector2(Infinity, Infinity); function onMouseMove(event) { mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1; mouse.y = -(event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1; } window.addEventListener("mousemove", onMouseMove, false); function updateMouseMarker() { raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera); const intersects = raycaster.intersectObject(ground); if (intersects.length > 0) { const intersectionPoint = intersects[0].point; mouseMarker.position.set(intersectionPoint.x, 0, intersectionPoint.z); } } function updateLine() { line.visible = mouseMarker.visible; // @ts-ignore line.geometry.setPositions([ ...new THREE.Vector3().toArray(), ...mouseMarker.position.clone().toArray() ]); // line.geometry.setFromPoints([enemy.position, mouseMarker.position]); line.computeLineDistances(); } function calcAngle(v1: THREE.Vector3, v2: THREE.Vector3) { return Math.acos(v1.dot(v2) / (v1.length() * v2.length())); } const toDegree = (radian: number) => (radian * 180) / Math.PI; const GUI = document.createElement("div"); GUI.style.cssText = "position: absolute; top: 16px; left: 32px; color: #fff; font-size: 1rem; white-space: pre-wrap"; document.body.appendChild(GUI); function updateGUI() { // const mouseToEnemy = mouseMarker.position.clone().sub(new THREE.Vector3()); // mouseToEnemy.y = 0; // // const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1).applyQuaternion(enemy.quaternion); // const enemyForward = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 1); // const angle = calcAngle(enemyForward, mouseToEnemy); // // const normal = enemyForward.cross(mouseToEnemy) // const normal = enemyForward.clone().cross(mouseToEnemy).normalize(); // GUI.textContent = const normalA = vecA.clone().cross(mouseMarker.position); const normalB = vecB.clone().cross(mouseMarker.position); arrowHelperA.setDirection(normalA); arrowHelperB.setDirection(normalB); } function animate() { requestAnimationFrame(animate); updateMouseMarker(); updateLine(); updateGUI(); controls.update(); renderer.render(scene, camera); } if (WEBGL.isWebGLAvailable()) { animate(); } else { const warning = WEBGL.getWebGLErrorMessage(); document.getElementById("container").appendChild(warning); }
移动蓝线可以看到,当蓝色向量在红绿两个向量间或者在红绿向量反向的向量间时,两个法向量方向是相反的,除此以外两个法向量的方向是相同的。再通过判断红色法向量是否与黄色法向量同向,来最终确定蓝色向量向量是否在红绿两个向量间。
三角菜单也可以使用相同的方法来解决,尽管二维向量通常没有叉积,但可以将二维向量放置在三维空间中,其中 Y 轴部分为 0。
总结
本文介绍了向量的点积和叉积,并探讨了它们在解决几何问题中的应用。
- 点积是向量在另一个向量方向上的投影和该向量模的乘积。它可以用于计算向量长度、夹角以及评估向量的相似性。
- 叉积是两个向量所在平面的法向量。它可以用于判断一个向量是否在两个向量夹角内的平面上。
这些概念和公式可以应用于各种实际问题,比如游戏中判断是否被敌人发现、实现菜单的交互效果以及计算物体之间的夹角等。
总的来说,向量的点积和叉积是解决几何问题的有力工具,可以帮助我们更好地理解和应用向量运算。